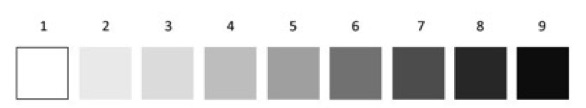
VALUE
Definition:
Value is the gradation from light to dark
across a surface, which is determined by
the lightness or darkness of the object and
the degree of light that strikes it.
The six categories of light:
highlight, light, shadow, core of shadow, reflected light, & cast shadow
Techniques for create value in drawing - artists whose work may is an example
1. tonal (smudging, erasing, rubbing or with washes) - Dine, Kollwitz, Tiepolo, Arikha
2. hatching (parallel, cross, contour, random) - Rembrandt, Durer, Ingres, Cadmus
3. scribbling (tightly tangled to loose and airy) - Giacometti, Abakanowicz, Daumier
4. stippling (dots or rough textured paper) - Seurat
Uses of value:
1. Arbitrary
a. to create focal point
b. to balance areas
c. to imply movement, pattern, direction
d. to organize composition
2. Descriptive
a. to create physical structure - volume or planes
b. to indicate weight - the response to gravity, darker values at base
c. to portray the light source -
highlight, light, shadow, core of shadow, reflected light, & cast shadow
d. to impart space
1. actual: light to dark or foreground, middle-ground, & background
2. flat or patterned
3. negative or reversed
Value scale:
High/light light (step 1-3)
Middle mid range (step 4-6)
Low/dark dark (step 7-10)
two-step B & W
three step B & W and gray
five step B & W and 3 grays
Exercises:
1) Reduce an image to two-step value. Google Notan on YouTube.
2) Draw an egg with one strong light source using the 4 techniques for creating value: tone, hatching, scribble, stippling.
3) Tone a paper with charcoal to a middle value gray by rubbing and blending to create a continuous tone. Erase out highlights. The figure should be lit with a single strong light from
directly above, or from below (stage lighting).
4) Incorporate a representative gray scale in a drawing.
Ellen Soderquist, © 1995